KORUZA alignment algorithm - revised
With development of the new KORUZA 1.0 prototype, offering greater flexibility in the unit adjustment, collimating process and pointing accuracy, we started developing a new version of the so called ‘Alignment algorithm’. Previous version, already successfully tested on the older system, KORUZA 5 Prototype, was designed to automatically fine-adjust pointing direction in order to optimise the link margin, either during initial alignment process or on operating link.
Analysis of the signal power over period of time and correlation to various weather effects, manly sudden changes in temperature, suggested much simpler and robust algorithm can be used on the new system, which in comparison to older version, is not as susceptible to mechanical errors due to temperature variations.
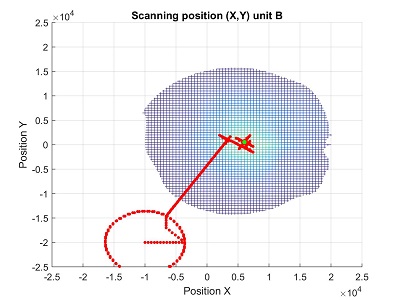
As before, the new design is first being tested in a Matlab simulation, using a beam scan of the new unit to simulate the link performance and the relationship between motors movements and optical link as realistically as possible. Beside the simplicity, the new algorithm features simultaneous alignment of the two units and takes into the account received and emitted power from both units. Testing under various settings, such as finding optimal position when located far from the source, re-alignment in the case of beam drifting and sudden change in the position of the beam on one or both units has so far showed encouraging results.
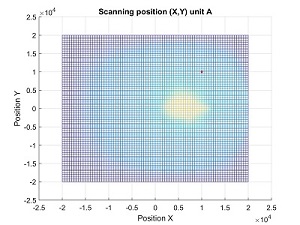
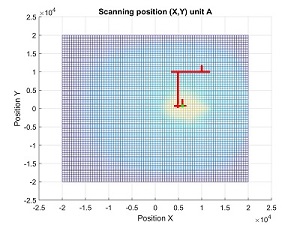
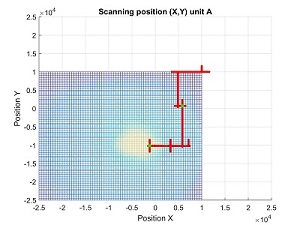
In the above plots we can see initial position, first alignment and re-alignment once the beam has moved.
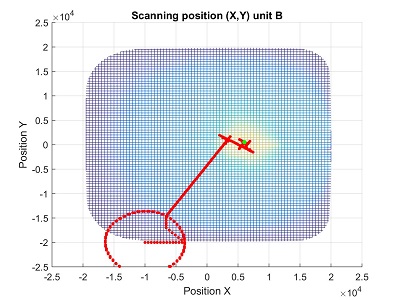
The algorithm responds well even in the case of gradual loss of the signal, such as in case of fog. The above two figures show alignment of one unit before and after gradual decrease of power has been introduced.
We are planning to develop universal implementation for embedded system shortly and later, once the satisfactory level of performance is achieved, implement it on the operational unit.